Davao Region
| Region XI Davao Region,Rehiyon ng Dabaw |
|
|---|---|
| — Region — | |
 |
|
| Country | Philippines |
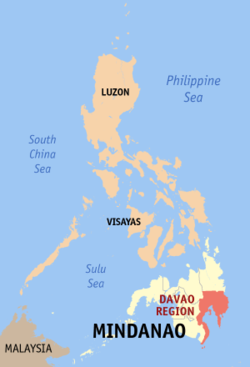
| Island group | Mindanao |
| Regional center | Davao City |
| Area | |
| - Total | 20,244 km2 (7,816.3 sq mi) |
| Population (2007) | |
| - Total | 4,156,653 |
| - Density | 205.3/km2 (531.8/sq mi) |
| Time zone | PST (UTC+8) |
| Provinces | 4 |
| Cities | 6 |
| Municipalities | 44 |
| Barangays | 1160 |
| Cong. districts | 11 |
| Languages | Cebuano, Davaoeño dialect of Chabacano, Mandayan, Dibabawon, Mansakan, Manobo, Tagalog, Ilokano, others |
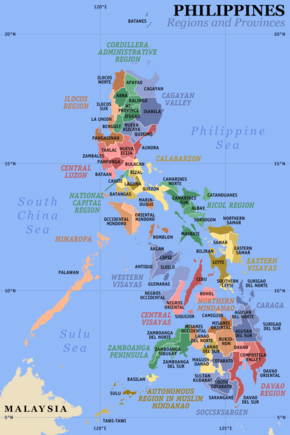
Davao Region, designated as Region XI, is one of the regions of the Philippines, located on the southeastern portion of Mindanao. Davao Region consists of four provinces, namely: Compostela Valley, Davao del Norte, Davao Oriental, and Davao del Sur. The region encloses the Davao Gulf and its regional center is Davao City. Davao is the Hispanicized pronunciation of daba-daba, the Bagobo word for "fire" (the Cebuano translation is "kalayo").
Contents |
History
Region XI was originally called Southern Mindanao, and in addition to the three Davao provinces also included Surigao del Sur and South Cotabato. At that time, Compostela Valley was still part of Davao del Norte. Republic Act No. 7225, ratified on March 16, 1992, created the province of Sarangani from South Cotabato. Then, Republic Act No. 7901, signed on February 3, 1995, by President Fidel V. Ramos transferred Surigao del Sur into the newly created region of Caraga (Region XIII). Finally, on September 19, 2001, President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo's Executive Order No. 36 reorganized the regions and provinces in Mindanao. This moved South Cotabato and Sarangani to SOCCSKSARGEN region and renamed Southern Mindanao as Davao Region.
This region also bears the nickname Silicon Gulf.
Cultural Groups
The region is an in-migration area, with a mixture of migrants, which include Cebuanos (making up the majority), Ilonggos and Ilocanos. Its ethnic groups include Manobos, Bagobos, Mansakas, Maguindanon, Kagans and Tirurays.
Climate
The region has a generally uniform distribution of rainfall through the year. It lies outside the typhoon belt.
Natural Resources
Aside from its forestland and fertile fields, Southern Mindanao has mineral resources of chromite, iron, nickel, and manganese, gold, copper and other non-metallic minerals. Five of the major fishing grounds of the Philippines are located in the region..
Economy
While the region’s economy is predominantly agri-based, it is now developing into a center for agro-industrial business, trade and tourism. Its competitive advantage is in agri-industry as its products, bananas, pineapples, fresh asparagus, and fish products are exported abroad. The region can be a vital link to markets in other parts of Mindanao, Brunei Darussalam and parts of Malaysia and Indonesia. There is also a small but growing call center sector.
There is a gradual shift to industrialization as shown with industry’s growth rate of 8.1% in 1996. Other economic activities are mining, fishery, forestry and agriculture.
Facilities
The region’s principal ports are the Sasa International Seaport in Sasa, Sta. Ana Pier in the Chinatown District, Panabo Seaport in Davao del Norte, and Mati Seaport in Davao Oriental. Infrastructure developments in the cities within the region are considered excellent.
The airport in Davao City is the largest and most developed in Mindanao. The region is accessible by land, air and sea. The region has adequate communications facilities, reliable power and an abundant water supply.
Political Divisions
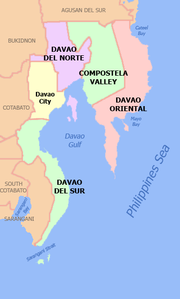
Davao Region is subdivided into 4 provinces and Davao City.
| Province/City | Capital | Population (2007) |
Area (km²) |
Pop. density (per km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compostela Valley | Nabunturan | 637,366 | 4,666.93 | 124.3 |
| Davao del Norte | Tagum City | 847,440 | 3,462.82 | 214.8 |
| Davao del Sur | Digos City | 822,406 | 3,934.01 | 192.9 |
| Davao Oriental | Mati City | 486,104 | 5,164.46 | 86.4 |
| Davao City | — | 2,363,337 | 2,443.61 | 469.4 |
Component Cities
- Digos City, Davao del Sur
- Island Garden City of Samal, Davao del Norte
- Panabo City, Davao del Norte
- Tagum City, Davao del Norte
- Mati City, Davao Oriental
Highly Urbanized City
- Davao City, Davao Region
|
|||||||||||